What Happens During Cytokinesis In Animal Cells.
seven.iii: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and Cytokinesis
- Folio ID
- 16755
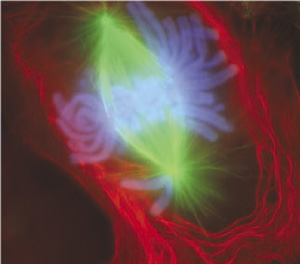
Can you gauge what this colorful image represents? Information technology shows a eukaryotic cell during the procedure of jail cell division. In particular, the image shows the nucleus of the cell dividing. In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus divides earlier the cell itself splits in two; and before the nucleus divides, the prison cell's DNA is replicated, or copied. At that place must be two copies of the Deoxyribonucleic acid and so that each daughter cell will have a complete copy of the genetic material from the parent cell. How is the replicated DNA sorted and separated so that each daughter cell gets a complete prepare of genetic material? To answer that question, you first demand to know more most DNA and the forms it takes.
The Forms of DNA
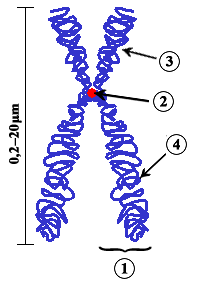
Except when a eukaryotic cell divides, its nuclear Dna exists equally a grainy fabric chosen chromatin. Only when a cell is virtually to split and its DNA has replicated does DNA condense and coil into the familiar X-shaped form of a chromosome, like the one shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). Considering Dna has already replicated, each chromosome really consists of 2 identical copies. The two copies of a chromosome are called sister chromatids. Sis chromatids are joined together at a region called a centromere.
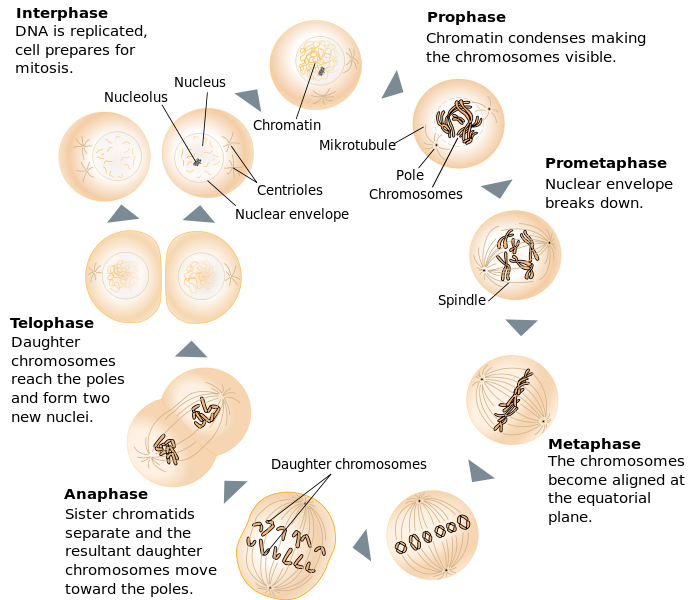
The process in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides is called mitosis. During mitosis, the two sister chromatids that make up each chromosome carve up from each other and motility to opposite poles of the cell. Mitosis occurs in four phases. The phases are called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. They are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{iii}\) and described in detail below.
Prophase
The beginning and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. In brute cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Centrioles are pocket-size organelles found only in eukaryotic cells that assistance ensure the new cells that course after cell division each contain a complete set of chromosomes. Equally the centrioles motion apart, a spindle starts to grade betwixt them. The blue spindle, shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{iv}\), consists of fibers made of microtubules.
Metaphase
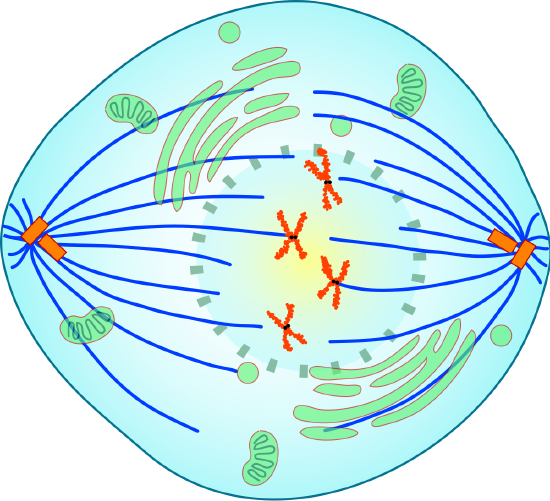
During metaphase, spindle fibers fully attach to the centromere of each pair of sis chromatids. Equally yous can see in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\), the sis chromatids line up at the equator, or center, of the cell. The spindle fibers ensure that sister chromatids volition divide and go to different girl cells when the jail cell divides. Some spindles practise not adhere to the kinetochore protein of the centromeres. These spindles are chosen non-kinetochore spindles that help in the elongation of the prison cell. This is visible in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\).
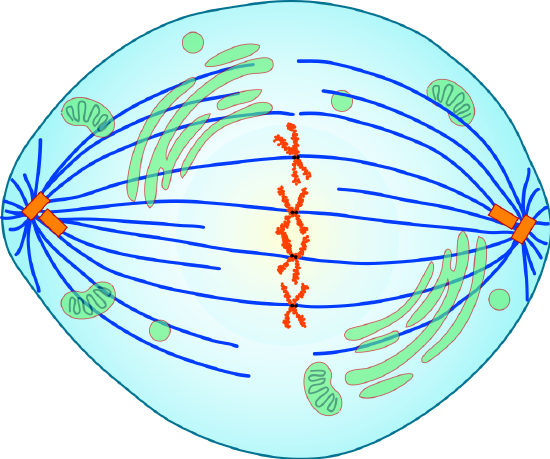
Anaphase
During anaphase, sister chromatids split and the centromeres divide. The sis chromatids are pulled autonomously by the shortening of the spindle fibers. This is a little like reeling in a fish past shortening the fishing line. One sis chromatid moves to 1 pole of the cell, and the other sister chromatid moves to the contrary pole (encounter Figure \(\PageIndex{six}\)). At the finish of anaphase, each pole of the cell has a consummate set of chromosomes
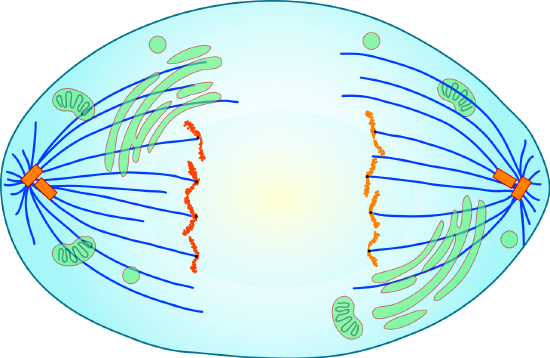
Telophase
The chromosomes reach the opposite poles and begin to decondense (unravel), relaxing once again into a stretched-out chromatin configuration. The mitotic spindles are depolymerized into tubulin monomers that will exist used to assemble cytoskeletal components for each daughter prison cell. Nuclear envelopes course effectually the chromosomes, and nucleosomes appear inside the nuclear area (see Figure \(\PageIndex{seven}\).
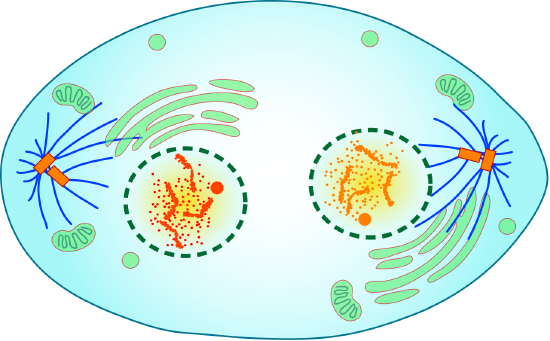
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the final phase of cell division in eukaryotes likewise as prokaryotes. During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits in 2 and the cell divides. The procedure is different in plant and animal cells, as y'all can run across in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\). In animate being cells, the plasma membrane of the parent prison cell pinches in along the cell's equator until two girl cells form. In the plant cells, a cell plate forms along the equator of the parent cell. So, a new plasma membrane and prison cell wall course along each side of the jail cell plate.

Review
- Depict the different forms that Deoxyribonucleic acid takes earlier and during cell division in a eukaryotic cell.
- Identify the four phases of mitosis in an beast prison cell, and summarize what happens during each stage.
- Explain what happens during cytokinesis in an animal prison cell.
- What are the primary differences between mitosis and cytokinesis?
- The familiar Ten-shaped chromosome represents:
- How DNA always looks in eukaryotic cells
- How Deoxyribonucleic acid in eukaryotic cells looks once it is replicated and the prison cell is about to divide
- Female person sex chromosomes only
- How DNA appears immediately afterward cytokinesis
- Which of the following is not part of a chromosome in eukaryotic cells?
- Centriole
- Centromere
- Chromatid
- Dna
- What practice you think would happen if the sister chromatids of i of the chromosomes did not split up during mitosis?
- Put the following processes in order of when they occur during cell segmentation, from first to final:
- separation of sister chromatids
- Deoxyribonucleic acid replication
- cytokinesis
- lining up of chromosomes in the center of the cell
- condensation and coiling of Deoxyribonucleic acid into a chromosome
- Why exercise you recall the nuclear envelope breaks downward at the kickoff of mitosis?
- What are the fibers fabricated of microtubules that adhere to the centromeres during mitosis are called?
- True or Simulated. Chromosomes brainstorm to uncoil during anaphase.
- True or False. During cytokinesis in beast cells, sis chromatids line up forth the equator of the prison cell.
- Truthful or False. Later on mitosis, the upshot is typically 2 daughter cells with identical DNA to each other.
Explore More
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Book:_Human_Biology_%28Wakim_and_Grewal%29/07:_Cell_Reproduction/7.3:_Mitotic_Phase_-_Mitosis_and_Cytokinesis
Posted by: suzukiwhourpel2001.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Happens During Cytokinesis In Animal Cells."
Post a Comment